- All
- Product Management
- News
- Introduction
- Enterprise outlets
- FAQ
- Enterprise Video
- Enterprise Atlas
Decoding the new food ingredient track for functional foods
With the rapid development of food science and technology, the globalization of food supply, and the demand for more food sources, the sources, types, and range of food ingredients are constantly expanding. Food ingredients are born in response to the needs of the public, thus the appropriate use of food ingredients has become an objective necessity for current development. Therefore, in order to standardize the development and application of food ingredients and ensure food safety,"New Food Ingredients"this concept has gradually come into the public eye.
01
Concept Analysis - What are New Food Ingredients?
With the reform of China's new food ingredient management system, the name of new food ingredients has undergone a change from "New Resource Food" to "New Food Ingredients". The connotation of the concept of new food ingredients has also changed accordingly. On October 1, 2013, the "Management Measures for the Safety Review of New Food Ingredients" (formulated by the National Health and Family Planning Commission) came into effect, and on the same day, the "Management Measures for New Resource Food" was abolished. Since then, the term new food ingredients has replaced the term new resource food. New food ingredients refer to the following items that have no traditional eating habits in China:
(1) Animals, plants, and microorganisms;
(2) Components isolated from animals, plants, and microorganisms;
(3) Food components whose original structure has changed;
(4) Other newly developed food ingredients.
Among them, "traditional eating habits" refers to a certain food that has a history of production and operation as a standardized or non-standardized packaged food for more than 30 years within a provincial jurisdiction and has not been included in the "Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China."
At the same time, this method stipulates that new food ingredients must comply with the provisions of the "Food Safety Law" and relevant laws, regulations, and standards, and must not pose any acute, subacute, chronic, or other potential health hazards to the human body.
02
Regulatory Support - Management System Gradually Improved
China's new food ingredient management system has roughly gone through three main stages: the "Management Measures for New Resource Food Hygiene" during the trial period of the Food Hygiene Law, the "Management Measures for New Resource Food Hygiene" and the "Management Measures for New Resource Food" during the Food Hygiene Law period, and the relevant regulations on new food ingredients during the Food Safety Law period (revised in 2015).
In 1983, China promulgated the Food Hygiene Law (trial), which stipulated in Article 22: Food produced using new resources must be approved by health authorities, thereby initially establishing the basic management system for new resource food.
In 1987, to facilitate the implementation of the Food Hygiene Law (trial), the former Ministry of Health issued the "Management Measures for New Resource Food Hygiene," which made specific requirements for the approval process of new resource food.
In 1990, the former Ministry of Health revised the "Management Measures for New Resource Food Hygiene" and formulated the "Approval Process for New Resource Food." In 1995, the Food Hygiene Law was officially implemented, which stipulated in Article 20 that food produced using new resources must be submitted for approval according to the prescribed procedures before production.
In 2007, the former Ministry of Health issued and implemented the "Management Measures for New Resource Food," which defined new resource food, safety evaluation, application, and approval, among other aspects. It also formulated supporting regulations such as the "Safety Evaluation Procedures for New Resource Food" and the "Regulations on the Declaration and Acceptance of Hygiene Licenses for New Resource Food," incorporating relevant requirements of the Administrative Licensing Law.
In 2009, China promulgated and implemented the Food Safety Law, which proposed in Article 44 that the production of food using new food ingredients should apply to the former Ministry of Health, and approval can only be granted after safety assessment meets food safety requirements.
In 2013, the former National Health and Family Planning Commission issued and implemented the "Regulations on the Declaration and Acceptance of New Food Ingredients" and the "Management Measures for the Safety Review of New Food Ingredients" (hereinafter referred to as the "Management Measures"), redefining new food ingredients and modifying the review procedures and safety evaluation requirements.
In 2015, China revised the Food Safety Law, retaining relevant provisions for the management of new food ingredients in Article 37.
03
Innovative Applications - New Food Ingredients Open a New Chapter in Future Diets
From 2021 to September 2022, a total of 13 new food ingredients were approved by the National Health Commission, including 2 strains that can be used in infant food: Bifidobacterium longum subsp. BB536 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus MP108. The detailed approval information for each ingredient is as follows:
Guanshan Cherry Blossom is the flower of the Guanshan Cherry (Cerasus serrulate ‘Sekiyama’) from the Rosaceae family, which has a long history of consumption in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, China, and is widely consumed as a vegetable or food ingredient. China began to introduce and cultivate Guanshan Cherry in the 1990s, and it is now widely cultivated in China, with consumption reported in provinces such as Shandong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu. Both dried and fresh products are edible. The food safety indicators for this ingredient are implemented according to the provisions for other vegetable products in China's current national food safety standards.
Guanshan Cherry Blossom has good antioxidant effects, and making it into functional beverages or formulations is beneficial for daily dietary supplementation. From Chuangyuan Biotechnology,Shuiyang Huayong Guanshan Cherry Blossom Sugar Drinkis a beauty-focused beverage that adds cherry blossom extract, with its main active substances being the contained cherry blossom glycosides and cherry blossom flavonoids, which can promote sugar metabolism. In addition, each bottle also contains 6000mg of fish collagen peptides, promoting collagen regeneration and revitalizing skin from within.

Shuiyang Huayong Guanshan Cherry Blossom Sugar Drink
Disodium Pyrroloquinoline Quinone, abbreviated as PQQ, is made from 6-amino-5-methoxy-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester and 2-oxopentenedioic acid dimethyl ester through a series of processes including coupling cyclization, quinoline ring formation, oxidation, ester hydrolysis, and purification. Disodium Pyrroloquinoline Quinone naturally exists in various foods such as milk, eggs, and spinach. The purity of this declared product is ≥98.0 g/100 g (on a dry basis).
Pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium salt is managed in the United States as a substance that is 'generally recognized as safe (GRAS)' and can be used as an ingredient in energy drinks, sports drinks, electrolyte drinks, and other foods; in the European Union and Canada, it is classified as a dietary supplement or natural health product. The recommended intake of this product is ≤20 mg/day (i.e., for a product with a pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium salt content of 98.0 g/100 g, the recommended intake is ≤20 mg/day; for products exceeding this content, the intake should be calculated based on the actual content). Usage scope and maximum usage amount: beverages (40 mg/kg, solid beverages calculated based on the liquid mass after preparation). The food safety indicators for this ingredient are implemented according to the announced regulations.
The biological functions of PQQ mainly focus on two aspects: first, it can support the growth and development of mitochondria and stimulate rapid cell growth in the human body; second, it has excellent antioxidant properties, helping to eliminate free radicals and reduce cell damage. These two major functions give it a powerful role in brain health, cardiovascular health, and metabolic function health. Since the human body cannot synthesize PQQ, it can be supplemented through dietary supplements, which are usually in powder form and prepared through microbial fermentation.
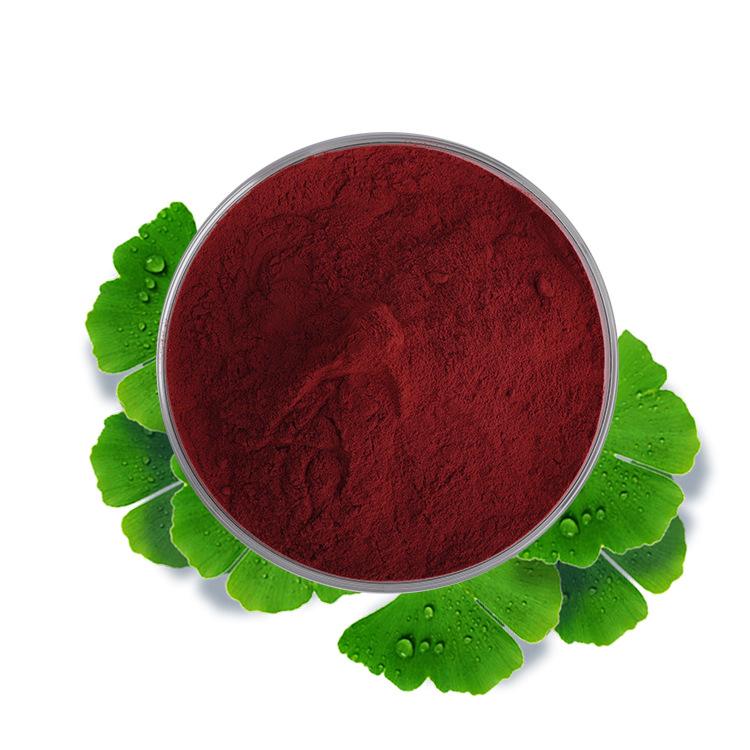

Pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium salt [PQQ] (image source from the internet)
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii belongs to the Chlamydomonadaceae family and the Chlamydomonas genus. It is produced through processes such as algal strain cultivation, heterotrophic expansion in fermentation tanks, and drying. The main nutritional components include protein, carbohydrates, fats, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, with protein content ≥30.0% and crude polysaccharides ≥10.0%.
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is classified as a 'generally recognized as safe' substance in the United States and can be used as a dietary protein source; it has been approved for use as a food ingredient in Singapore; and it is allowed to enter the market for sale in Hong Kong, China. The food safety indicators for this ingredient are implemented according to the current national food safety standards for algae and their products in China.
Bifidobacterium longum subsp. (originally named 'Bifidobacterium longum') has been included in the list of strains that can be used in food in China and has also been included in the recommended list of qualified biological agents by the European Food Safety Authority (QPS) and in the 'Microbial Species Directory of Technical Necessity in Fermented Foods' in the Bulletin of the International Dairy Federation (Bulletin of the IDF 455/2012).
Bifidobacterium longum subsp. BB536 (Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BB536) is isolated from the intestines of healthy infants, and this strain has been approved for use in infant food in the United States and Japan. Multiple clinical studies on infants conducted domestically and internationally have proven that this strain has good safety for consumption. The food safety indicators for this strain's raw materials should comply with relevant standards in China.
Bifidobacterium longum (image source from the internet)
Sugarcane polyphenols are derived from sugarcane through processes such as pressing, filtering, and extraction, followed by the removal of excess sugars and salts to obtain sugarcane molasses. They are then processed into powdered substances using water and ethanol as extraction solvents, followed by filtration, vacuum concentration, ion exchange, and spray drying; or they can be processed into liquid substances through filtration and vacuum distillation.
Its main characteristic component is total polyphenols. The United States has classified it as a 'generally recognized as safe' substance, the European Union allows it to be used as a food ingredient, Australia and New Zealand manage it as a regular food, and Taiwan, China has used it as a food ingredient. The recommended intake for this product is: for powdered form with a total polyphenol content of 200 g/kg, the recommended intake is ≤1 gram/day; for liquid form with a total polyphenol content of 14.8 g/kg, the recommended intake is ≤10 grams/day, with amounts exceeding these levels calculated based on actual content.
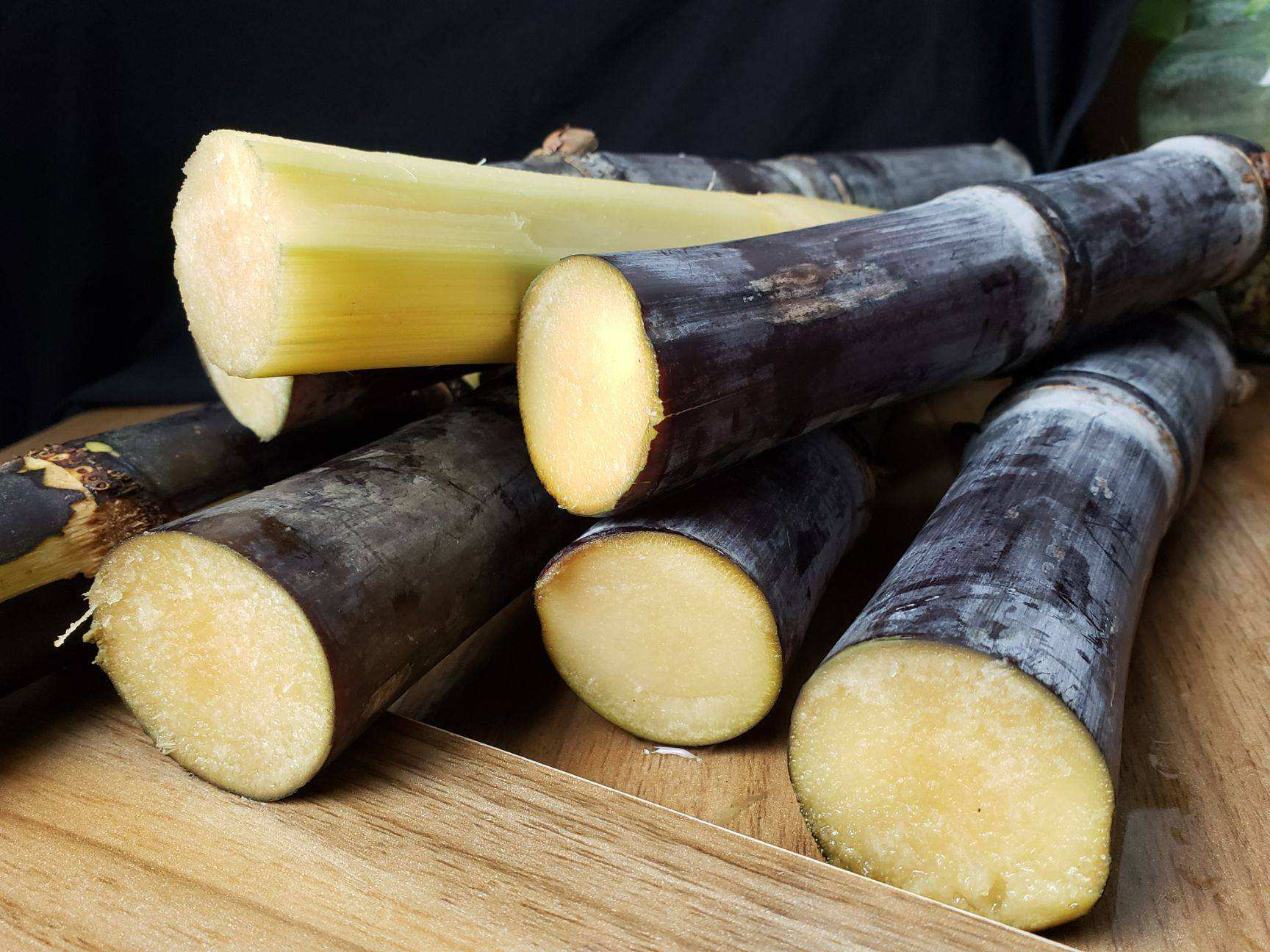

Sugarcane (image source from the internet)
Cicada flower (Isaria cicadae Miq.) fruiting body, also known as cicada stick bundle fruiting body, has a history of consumption in provinces such as Zhejiang, Guangdong, Fujian, and Sichuan in China. The cicada flower fruiting body (artificially cultivated) is produced by inoculating cicada flower mycelium onto a culture medium for artificial cultivation, followed by harvesting the fruiting bodies (i.e., sporophore bundles), drying, and other processes. It contains protein, polysaccharides, and other components, with a recommended intake of ≤3 grams/day (based on dry weight).
The food safety indicators for this ingredient are implemented according to the current national food safety standards for edible fungi in China. In addition, aflatoxin B1, aflatoxin B2, aflatoxin G1, aflatoxin G2, deoxynivalenol, ochratoxin A, and zearalenone must not be detected; the content of Beauvericin should be ≤3 mg/kg.

Cicada flower and cicada flower fruiting body powder (image source from the internet)
Sodium hyaluronate is produced by fermenting a culture medium containing glucose, yeast powder, and peptone using Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus. It is the sodium salt of a glycosaminoglycan composed of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine disaccharide units, and is a linear macromolecule polysaccharide.
In 2008, China approved sodium hyaluronate as a new resource food, with its usage scope as a health food ingredient. Currently, sodium hyaluronate and products containing it as a main ingredient are allowed to be added to food or dietary supplements in Japan, South Korea, the United States, the European Union, Australia, New Zealand, and Brazil. Based on the approval status in other countries and international organizations, this product applies to expand its usage scope to include dairy and dairy products, beverages, alcoholic beverages, cocoa products, chocolate and chocolate products (including chocolate and products with cocoa butter substitutes), as well as candies and frozen drinks. There is insufficient safety data for consumption in infants, pregnant women, and breastfeeding women; therefore, based on the principle of risk prevention, these populations should avoid consumption, and labels and instructions should indicate unsuitable populations and recommend an intake of ≤200 mg/day.
Launched by Chuangyuan BiotechnologyYunshang Huayong™ Sodium Hyaluronate Collagen Peptide Water Light DrinkAdded a combination of three golden ingredients: sodium hyaluronate, elastin peptides, and collagen peptides, with each bottle containing 100mg of high-purity, water-soluble small molecule hyaluronic acid, creating a three-dimensional network for the skin.

Water Bloom™ Sodium Hyaluronate Collagen Peptide Water Light Drink
Lactobacillus rhamnosus subsp. rhamnosus belongs to the Lactobacillaceae family and the Lactobacillus genus, and is a lactic acid bacterium that can produce kefir polysaccharides. The strain appears as a white or slightly yellow powder to fine particles. This strain has been included in the recommended list of qualified biological agents by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and is listed in the International Dairy Federation Bulletin (Bulletin of the IDF 455/2012) as a 'microbial species with technical necessity in fermented foods', and has been approved for use in Canada and South Korea. Safety assessment studies conducted domestically and internationally have proven that this strain has good edible safety. The food safety indicators for the raw materials of this strain should comply with relevant national standards.
β-1,3/α-1,3-Glucan is made from sucrose as the main raw material, fermented by Rhizobium pusense, followed by alcohol precipitation, filtration, separation, drying, and grinding processes. β-1,3/α-1,3-Glucan is a linear polysaccharide composed of 9 D-glucose units, formed by the connection of 7 β-1,3-D-glucose and 2 α-1,3-glucose. The content of β-1,3/α-1,3-Glucan in this product is ≥90 g/100g.
Currently, β-glucans derived from yeast, oats, barley, and other sources have been approved for use as food ingredients or food additives in several countries including the United States, Australia, and Japan. In China, β-1,3-Glucan was approved as a food additive in 2006, and yeast β-glucan and oat β-glucan were approved as new food ingredients in 2010 and 2014, respectively. The recommended daily intake of β-1,3/α-1,3-Glucan is ≤3 grams/day.

Yeast β-Glucan Raw Material Powder (Image source from the internet)
Dihydroquercetin (Dihydroquercetin) is a type of dihydroflavonol compound found in various plants. This product is made from the roots of artificially cultivated Larix gmelinii, processed through peeling, tearing, extraction, concentration, alcohol precipitation, supernatant concentration, extraction, re-concentration, crystallization, centrifugation, freeze-drying, and sieving. The EU has approved dihydroquercetin derived from larch as a new food ingredient, and Russia has approved it for use as a food ingredient and food additive. The recommended daily intake of this product is ≤100 mg/day (i.e., the recommended intake for 90% dihydroquercetin is 100 mg/day, and amounts exceeding this should be calculated based on actual content). Usage scope and maximum usage amount: beverages (20mg/L), fermented milk and flavored fermented milk (20mg/kg), cocoa products, chocolate, and chocolate products (70mg/kg). The food safety indicators for this raw material are implemented according to the announced regulations.
Lactobacillus rhamnosus MP108 (Lactobacillus rhamnosus MP108) is isolated from the intestines of healthy infants, and the strain appears as a white to light brown powder. Products containing this strain have been produced and marketed in Australia and can be used in infant food. Multiple clinical studies on infants conducted domestically and internationally have proven that this strain has good edible safety. The food safety indicators for the raw materials of this strain should comply with relevant national standards.
Lactobacillus rhamnosus has biological characteristics such as acid resistance, bile salt resistance, and resistance to various antibiotics. Its functional characteristics mainly include regulating intestinal flora, preventing and treating diarrhea, toxin excretion, and enhancing the body's immunity, which, combined with food science, has extremely high application value and development prospects.
Lactobacillus rhamnosus (Image source from the internet)
Nannochloropsis (Nannochloropsis gaditana) belongs to the family Nannochloropsaceae and the genus Nannochloropsis, with small algal bodies that are usually green or yellow-green. Foods containing this algae are sold in countries such as the United States, Chile, and Canada. This algae contains nutrients such as protein and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), with a recommended daily intake of ≤2 grams/day (based on dry weight). The food safety indicators for this raw material are implemented according to the current national food safety standards for edible algae.

Nannochloropsis Powder (Image source from the internet)
Rumex is a perennial herbaceous plant of the Rumex genus, developed from the introduction of Rumex K-1 and the wild Rumex from China. Rumex is cultivated and consumed in several provinces in China, including Hebei, Henan, Shandong, Shanxi, Shaanxi, and Gansu, with edible parts being the stems and leaves. It can be consumed in various ways such as salads, juices, stir-frying, tea, tofu, and noodles, with no reported adverse reactions from the population. The food safety indicators for this raw material are implemented according to the current national food safety standards for leafy vegetables.
04
Summary - New Choices for Functional Food Ingredients in the Future
Although the approval process is lengthy, in recent years, new food ingredients have been accepted, publicly solicited for opinions, and successfully approved each year. These approved new food ingredients can be classified by their source and properties intofungi, functional sugars, plant-based ingredients, plant extracts, and other 8 categories. A large number of studies have shown that many approved new food ingredients have various health benefits, and these new food ingredients are increasingly appearing in candies, yogurts, beverages, and other food products, gradually gaining public recognition.
Although there are still many ingredients in the new food ingredient directory that are not well known to consumers and need further promotion and development, with the deepening research on the health functions of new food ingredients, more and more new food ingredients are entering public life, opening up new ways for the public to lead a healthy life. These ingredients will also become powerful tools for companies to win future markets.
Appendix: List of New Food Ingredients (New Resource Foods) (as of September 30, 2022)
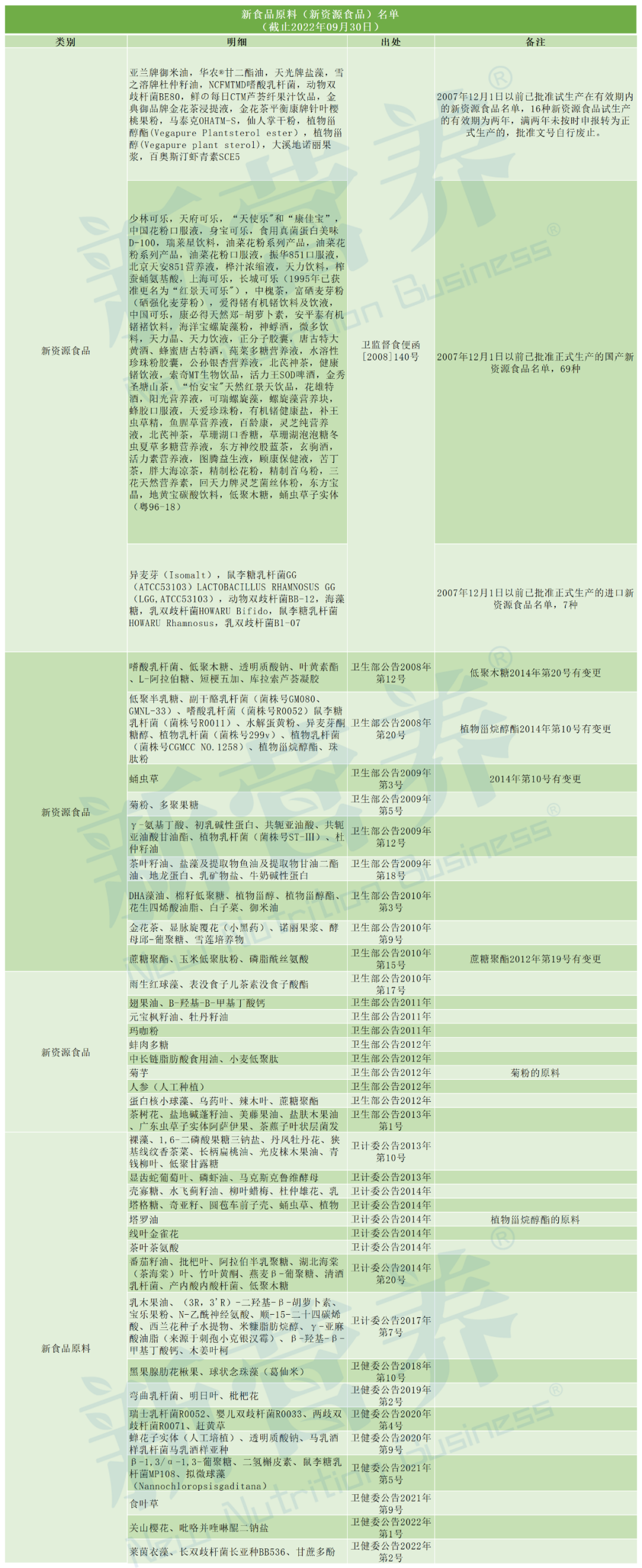
Source: New Nutrition WeChat public account, authorized for reprint.
Some images are sourced from the internet. If there is any infringement, please inform us for deletion.
Food, ingredients, food safety, strains, new food ingredients, sodium hyaluronate, Guanshan cherry blossom
Related News


