All
- All
- Product Management
- News
- Introduction
- Enterprise outlets
- FAQ
- Enterprise Video
- Enterprise Atlas
The probiotic market is steadily developing, and there are three points of regulation worth paying attention to in the future!

Editor's Note
Today, the probiotic market has become a highly regarded field. As people's health awareness continues to rise, more and more individuals are beginning to pay attention to the benefits of probiotics and consider them an important part of their daily supplementation.
Today, we focus on the probiotic market together. We hope this article can provide some inspiration and assistance to industry professionals and readers.
The popularity of probiotics remains high,The global market is steadily developing.
The popularity of probiotics remains high, attracting continuous attention from consumers.The latest Google Trends data shows that the popularity of probiotics continued to remain high in 2022, consistent with the levels of 2021. According to a probiotic survey conducted by Kahnson in 2022, which included 16 countries and 160 million people, 75% of respondents reported being very familiar with or having some knowledge of probiotics, and 71% of consumers expressed a desire to learn more about probiotics. Additionally, 50% of respondents stated they were familiar or very familiar with the term 'gut microbiome.' This data indicates that, against the backdrop of increasing consumer health awareness, probiotics, as a functional ingredient that supports the gut microbiome, continue to attract consumer attention.
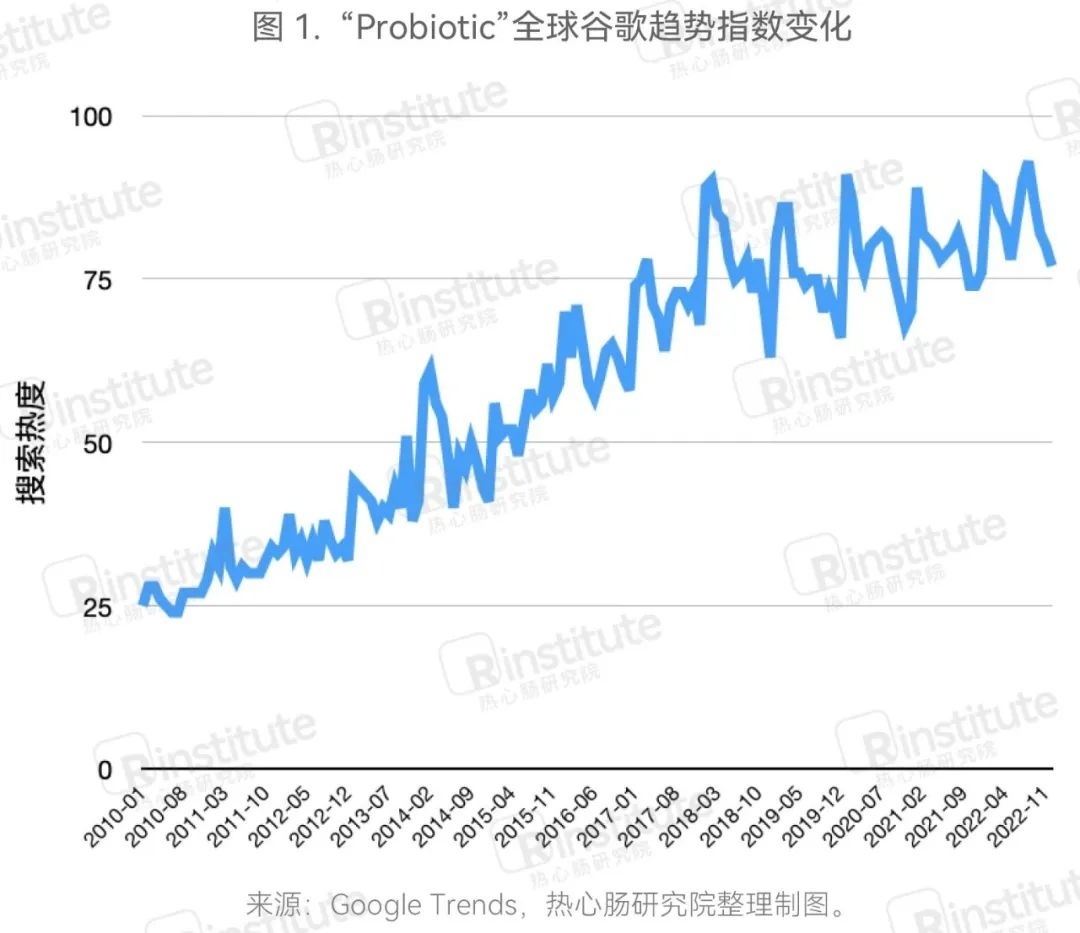
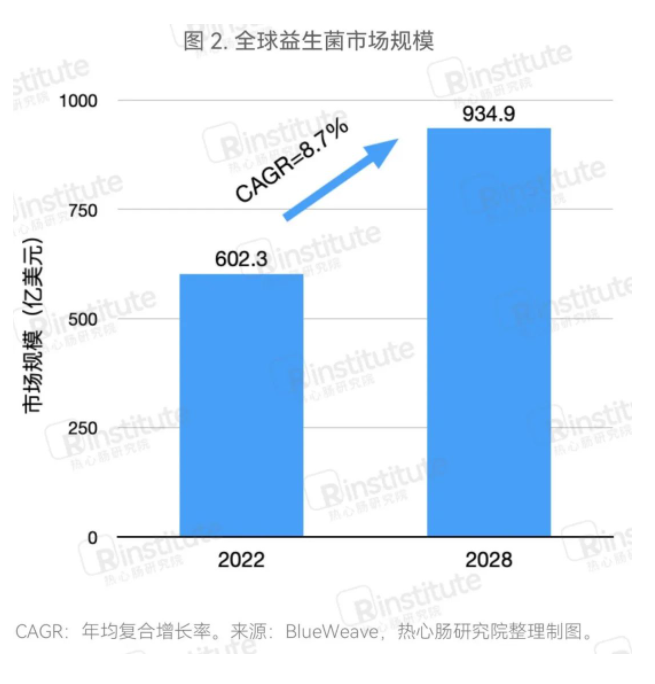
The global probiotic market is steadily developing, surpassing $60 billion in 2022.In 2022, the global probiotic market continued to grow. According to data from BlueWeave, the global probiotic market size reached $60.23 billion in 2022, and it is expected to grow at an annual compound growth rate of 8.7% from 2022 to 2030, reaching $93.49 billion by 2028. Due to digestive health and other benefits, probiotics are becoming increasingly popular worldwide, with significant increases in related demand. Additionally, manufacturers are continuously innovating and launching new probiotic products, providing consumers with more choices while further promoting the development of the probiotic market.
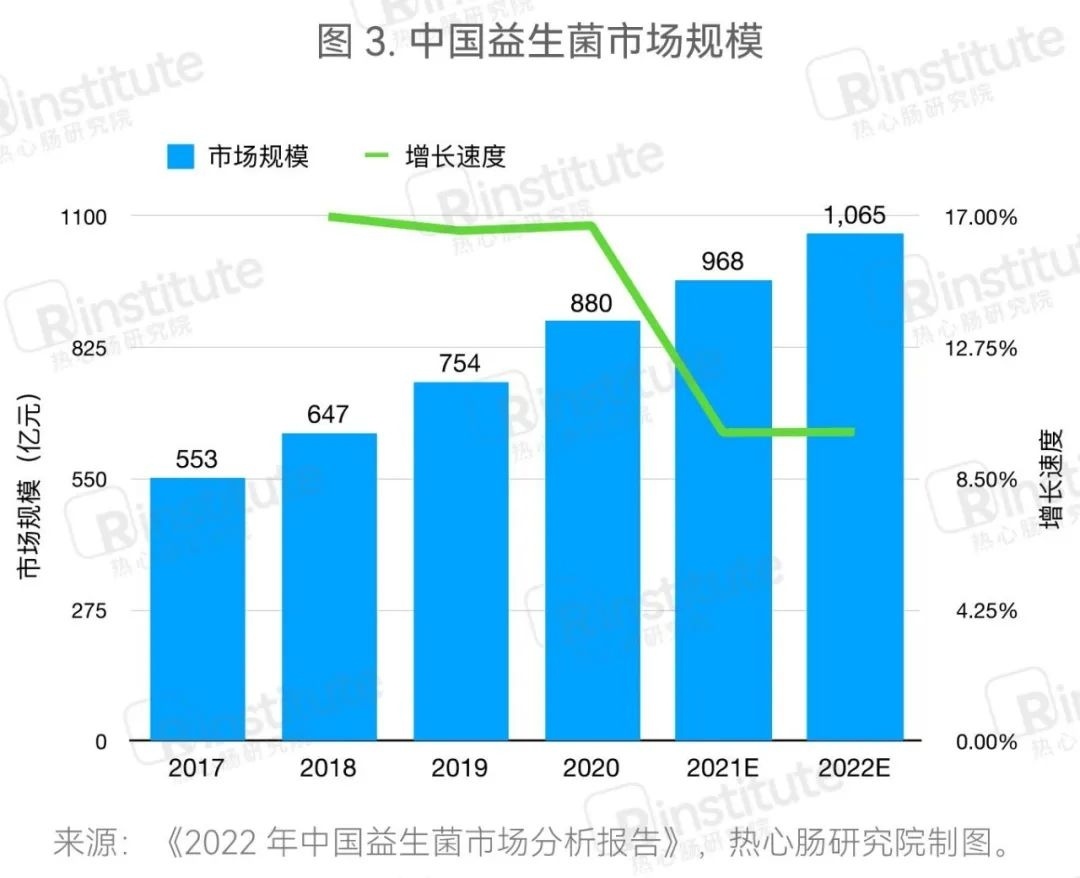
The market size in China continues to expand,but the growth momentum is slowing.
The market size in China continues to grow, but the growth rate is slowing.With ongoing in-depth research on probiotics, their applications are becoming increasingly widespread. Driven by downstream demand, China's probiotic market has maintained a steady growth trend, with the market size of the probiotic industry surpassing 100 billion yuan in 2022, reaching 106.5 billion yuan (estimated). However, it is worth noting that China's probiotic market has already taken shape, and compared to previous years, the growth rate has significantly slowed in recent years, with industry competition becoming increasingly fierce.
Consumer awareness is relatively high, and the pandemic has driven a surge in the popularity of probiotics.The 'China Probiotic and Prebiotic Consumer Research Report' released in 2022 shows that Chinese consumers have a high level of awareness of probiotics, with 70% of respondents indicating they know about probiotics, and 54% of respondents stating they are very or somewhat familiar with probiotics. The high awareness of probiotics among Chinese consumers can be attributed to various reasons, including but not limited to:
(1) The wave of microbiome research has driven the development of related fields, allowing more people to be exposed to relevant concepts;
(2) Companies and organizations in the probiotic field actively engage in science popularization education;
(3) The continuous enhancement of consumer health awareness, with more people actively seeking to understand components and products beneficial to gut health.
The scale of probiotic imports remains stable,while the scale of exports is rapidly expanding.
The trend of China's probiotic import value remains stable, with Denmark, the United States, and France as the main importing countries.From 2017 to 2022, the import value of China's probiotic industry has remained basically stable. In 2022, the total import value of probiotic products was 1.203 billion yuan, unchanged from 2021, with no significant changes. In terms of import sources, the main sources of probiotics imported by China in 2022 were Denmark, the United States, and France. Compared to 2021, the scale of probiotics imported from New Zealand slightly increased, while the proportion of probiotic strains imported from Taiwan decreased slightly, but the overall structure of import sources in 2022 showed no significant changes compared to 2021.
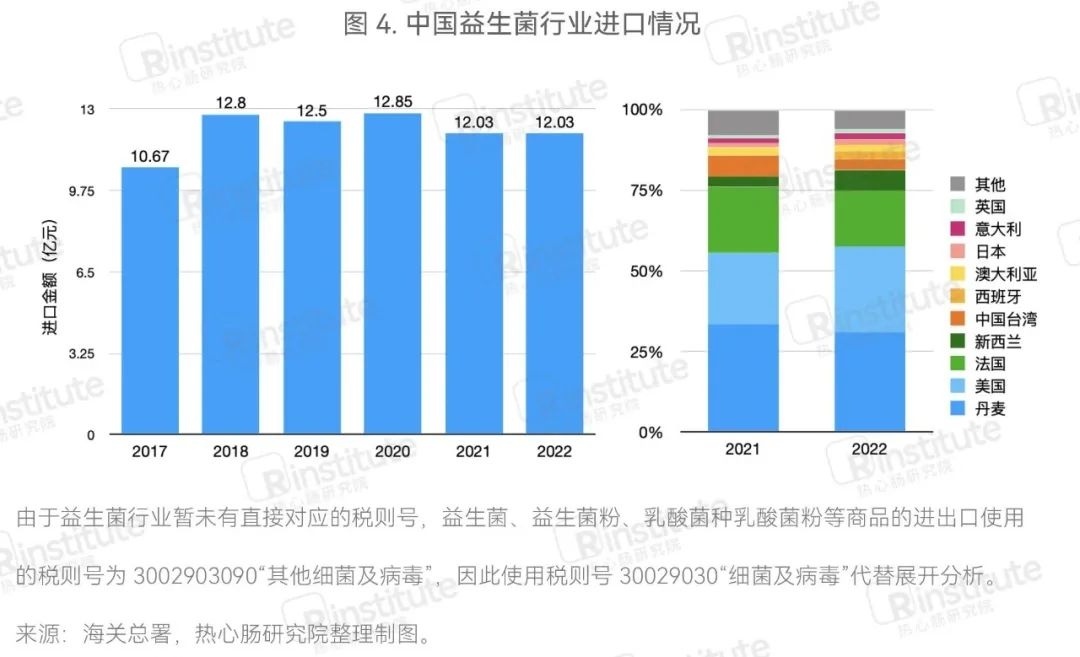
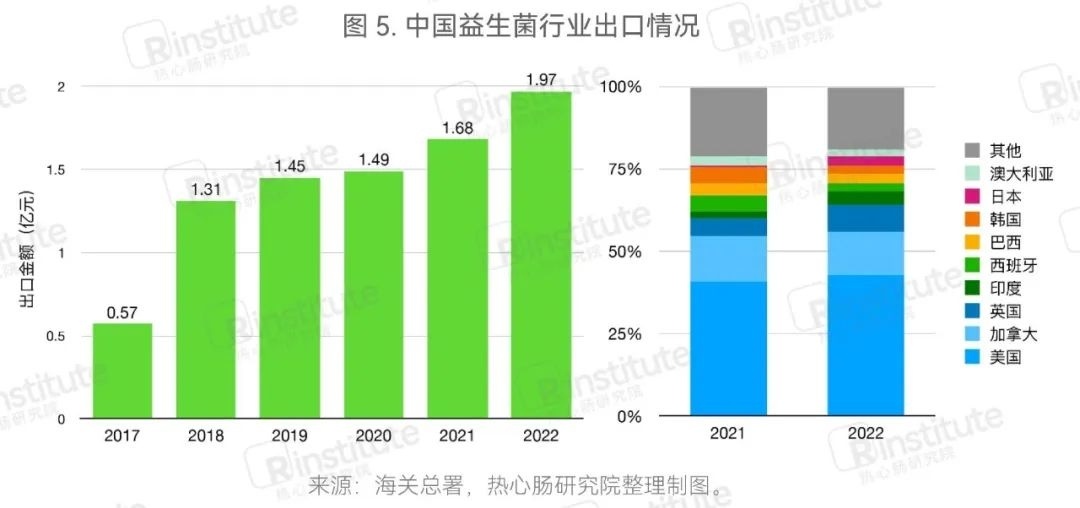
The export scale is rapidly expanding, with the UK and India showing a rapid increase in proportion.From 2017 to 2022, the export value of probiotic products has increased year by year, with the total export value of this category reaching 197 million yuan in 2022, a significant increase. The main export destinations for probiotic products are the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. Compared to 2021, the proportion of exports to the UK and India has significantly increased. Currently, as China's probiotic companies rapidly develop, more and more companies are beginning to export probiotic products to foreign markets or authorize production and sales abroad through cooperation.
Regulatory policies still need breakthroughs,and industry associations are taking frequent actions.
Looking back at 2022, the probiotic industry has seen many new developments in regulation.
In January 2022, the State Administration for Market Regulation issued the 'Announcement on Strengthening the Quality and Safety Supervision of Solid Beverages' (referred to as the 'Announcement'), further standardizing the labeling of solid beverages, strictly regulating the quality and safety of solid beverages, and effectively safeguarding consumers' legitimate rights and interests.The specific requirements are as follows:
1. The 'Announcement' stipulates that the product name of solid beverage products must not be the same as the names of special foods that have been approved and published; it should prominently indicate the specific name 'solid beverage' that reflects the true nature of the food on the product label, with the font size not smaller than other text on the same display panel (including trademarks, patterns, etc.).
2. The 'Announcement' emphasizes that protein solid beverages, plant solid beverages, special-purpose solid beverages, flavored solid beverages, and solid beverages containing edible strains provided directly to consumers should also indicate on the same display panel that 'this product cannot replace special medical purpose formula foods, infant formula foods, health foods, and other special foods' as a warning message, occupying no less than 20% of the area of the surface it is on, with the warning message text printed in bold font and having a significant color contrast with the background of the warning message area.
3. The 'Announcement' requires that solid beverage labels, instructions, and promotional materials must not use text or images to explicitly, implicitly, or emphasize that the product is suitable for specific groups such as minors, the elderly, pregnant and postpartum women, patients, or those with nutritional risks or malnutrition, nor should they use production processes, raw material names, etc., to explicitly or implicitly involve disease prevention, treatment functions, health functions, or meet the special needs of specific disease populations.
4. The 'Announcement' encourages industry associations and other social organizations to play a guiding and self-regulatory role in the industry, standardizing the production, sales, and promotional behaviors of enterprises; it encourages schools to strengthen food safety and nutrition education for minors and advocates for parents and other consumers to have a scientific understanding and rational consumption.

In May 2022, the China Nutrition and Health Food Association approved and released the group standard "Probiotic Food Viable Count Classification Specification" (T/CNHFA 006-2022), which took effect on May 28, 2022.This group standard applies to the classification of viable counts in probiotic foods such as powders and granules, and stipulates that only when the viable count (stored under the conditions indicated on the label for one-third of the shelf life) exceeds 50% can it be labeled as "Level 1 Viable Count".
In June 2022, the group standard "General Principles for Probiotics in Food" was officially released by the Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology.This group standard is based on the scientific consensus related to probiotics in China, while also referencing important scientific conclusions from international standards, regulations, and authoritative guidelines, marking a milestone in regulating probiotic raw materials and their scientific application in food.
In August 2022, the Probiotics Branch of the Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology released a scientific review on the "Dose-Effect Relationship of Probiotics".It pointed out that:(1) The intake of probiotics is a key factor for their health effects;
(2) Accurate counting of viable counts at the strain level is an important technical condition for measuring probiotic dosage;
(3) Existing research literature and international standards mainly recommend a probiotic intake of 10
-107CFU/day;11(4) The effective dose of probiotics varies by strain, and higher addition is not necessarily better;
(5) The clinical dosage of probiotics in different types of food is relatively stable;
(6) The health effects of probiotics do not depend on the number of strains combined, and should be based on scientific research on interactions between strains.
In August 2022, the National Health Commission announced updates to the "List of Microorganisms Allowed for Use in Food" and the "List of Microorganisms Allowed for Use in Infant Food."
The updated list adjusted the names of certain strains, including the addition of animal subspecies of Bifidobacterium animalis, renaming Bifidobacterium lactis to Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis; renaming Bifidobacterium longum to Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum, and renaming Bifidobacterium infantis to Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis, among others; 12 strains including Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus paracasei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Staphylococcus aureus were updated to different species.The basis for this list update is the latest research results from the international scientific community on the application of whole-genome sequencing technology in microbial taxonomy. The classification and management of the proposed updated strains also referenced the classifications and management of international organizations such as the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the International Dairy Federation (IDF), as well as relevant countries like Canada and Denmark, ensuring better alignment and consistency with international regulations, facilitating industry development.
In addition, the lists of microorganisms allowed for use in food and in infant food have also been updated.
In May 2022, Bifidobacterium longum subsp. BB536 was approved for use in infant food. In March 2023, Lactobacillus rhamnosus was included as a new food ingredient, allowed for use in fermented milk, flavored fermented milk, cheese, fermented dairy beverages, and lactic acid bacteria beverages (non-solid beverages), excluding infant food. In October 2023, Lactobacillus rhamnosus subsp. was approved for inclusion in the "List of Microorganisms Allowed for Use in Food," with a scope of use including fermentation processing of dairy and dairy products, fruit and vegetable products, and grain products, excluding infant food.Overall, the regulation of the probiotic industry is becoming stricter. In recent years, the probiotic industry, as an important part of China's food industry, has maintained a rapid development trend, but there are also issues such as improper use of probiotic concepts, difficulty in scientifically defining efficacy, and non-standard product labeling, which pose potential hazards and risks to the development of the probiotic industry.
In light of the recent development of the probiotic industry, we believe that the future trends in probiotic regulation and standardization will mainly include the following three points:1. Proper use of probiotic concepts:
Currently, many products on the market confuse the concept of lactic acid bacteria with probiotics, equating products that add lactic acid bacteria with those that add probiotics, and promoting them extensively. However, lactic acid bacteria and probiotics are not equivalent; not all lactic acid bacteria are probiotics, and not all probiotics are lactic acid bacteria. In the future, there may be increased regulatory efforts against such misuse and false advertising related to the health effects of probiotics.2. Stricter definitions of probiotic products:
Composite probiotic products are one of the main types of products in the current probiotic market. However, many composite probiotic products on the market do not contain only probiotic strains, yet they overly emphasize "probiotics" and their effects in product promotion. Additionally, considering the complex relationships between different strains, simply emphasizing the benefits of certain strains does not accurately reflect the benefits of composite probiotic products. Therefore, in the future, relevant standards may further clarify the definition of probiotic products.3. More standardized product labeling:
The release of the "Announcement on Strengthening Quality and Safety Supervision of Solid Beverages" fully reflects the strictness of product labeling regulation by relevant national departments. The types and quantities of probiotics can significantly impact probiotic products. Currently, many probiotic products have labeling issues such as unclear strains/strains and quantities. Considering the increasing strictness of regulation and consumers' growing desire to understand the specific components of probiotic products (such as the strains used), future regulation of product labeling may become more stringent and standardized.Source: Gut Industry WeChat Official Account, authorized for reproduction.
文章来源:肠道产业公众号 已获得转载授权

Previous Page
Related News


